What is Adenosine Deaminase?
Further Proteins Performing This Function
What is ADA deficiency?
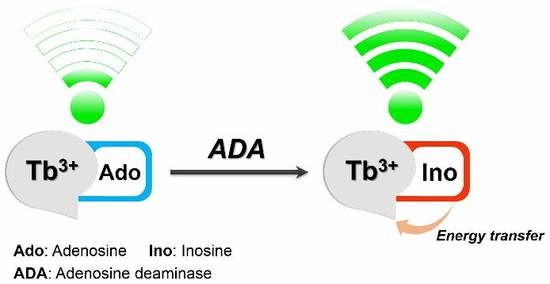
The function of the adenosine deaminase enzyme is to eliminate a molecule called deoxyadenosine, which is generated when DNA is broken down. Adenosine deaminase converts deoxyadenosine, which is toxic to lymphocytes, to another molecule called deoxyinosine, which is not harmful.
https://enzymes1.wixsite.com/website/post/what-are-the-enzymes-and-the-functions
https://penzu.com/public/19cbb5fb
https://all4webs.com/enzymesbio/home.htm
Molecular Anatomy Of Cellular Systems
Mutations in ADA2 can lead to polyarteritis nodosa and other vasculopathies, and certainly some patients with immunodeficiency have been identified (4–6). However, for the goal of this evaluation, we will go over only ADA1 encoded for by the ADA gene, because this is the enzyme that is implicated in ADA-SCID, and we will refer to it throughout as ADA. Lack of this enzyme leads to the accumulation of toxic metabolites causing extreme combined immunodeficiency (ADA-SCID), an autosomal recessive disorder. Lymphocytes are an critical element of the immune system and assist defend the body from infections. The function of the ADA enzyme is to convert a substance that is dangerous to lymphocytes (known as deoxyadenosine) to a non-dangerous substance. For the reason that of this make up, lymphocytes are unable to develop and fight infection, top to extreme combined immunodeficiency.- Significantly to her surprise, starch gel electrophoresis indicated that the red blood cells of the patient have been fully devoid of ADA enzyme activity!
- These have been fully unexpected findings, as there was no precedence for ADA deficiency in humans or for ADA playing an critical function in either the improvement or function of the immune system.
- It was hoped that she could shed light on the relationships among the family members of the patient by examining isozyme patterns for the enzyme ADA.
- The parents showed detectable, but reduced ADA activity, suggesting an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
- Subsequently, a second patient with extreme cellular immune deficiency was studied and also discovered to be ADA-deficient.
- Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency leads to an accumulation of toxic purine degradation by-solutions, most potently affecting lymphocytes, top to adenosine deaminase-deficient extreme combined immunodeficiency.
What are the products of Deamination?
Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency is an inherited disorder that damages the immune system and causes severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). The main symptoms of ADA deficiency are pneumonia, chronic diarrhea, and widespread skin rashes.
Adenosine Deaminase
Hematopoietic stem cell transplant has lengthy been established as the therapy of option, especially exactly where a matched sibling or well matched unrelated donor is readily available. Far more not too long ago, the use of gene addition techniques to right the genetic defect in autologous haematopoietic stem cells therapy has demonstrated immunological and clinical efficacy. This short article reviews the biology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and therapy of ADA-deficiency.Rna Editing By Mammalian Adars
PEG-ADA became the initially PEG-modified protein to be used as a therapeutic and opened the door for the development of further PEG-modified proteins that are in wide clinical use now Deaminase. Ultimately, ADA-deficient mice became an invaluable tool for the study of adenosine receptor signaling in chronic lung diseases and sickle cell illness. In conclusion, the discovery of ADA-deficiency as a lead to of SCID was ground-breaking for many reasons. Very first, it was the initially immunodeficiency illness for which the molecular defect was identified, producing it possible to make a molecular diagnosis each pre- and postnatally. Second, it underscored the significance of regular purine metabolism for the development of the immune system. Understanding the mechanisms of ADA-deficient SCID led to the development of ADA inhibitors and deoxyadenosine analogs for the therapy of hairy cell leukemia . Nevertheless, this method was effective in individuals with X-linked SCID mainly because the genetically modified cells had a selective benefit and sooner or later overgrew the remaining unmodified cells . This realization led to the hypothesis that gene therapy for ADA deficiency was unsuccessful mainly because individuals had been maintained on PEG-ADA as a sort of normal of care. This therapy removed the selective benefit that ADA-gene corrected cells would appreciate in an otherwise ADA-deficient host. Indeed, when the therapy protocols had been modified to get rid of the PEG-ADA, gene therapy for this disorder was effective, although it usually took a year or more for the quantity of gene-corrected T cells to reach maximal levels . Most states in the United States screen newborns for severe combined immune deficiency (SCID). It was hoped that she could shed light on the relationships amongst the family members members of the patient by examining isozyme patterns for the enzyme ADA. Significantly to her surprise, starch gel electrophoresis indicated that the red blood cells of the patient had been completely devoid of ADA enzyme activity! The parents showed detectable, but decreased ADA activity, suggesting an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance. Subsequently, a second patient with severe cellular immune deficiency was studied and also located to be ADA-deficient. It was already recognized that individuals with SCID could be cured by a BMT from a histocompatible donor. It was also recognized that individuals with only 10–12% of regular ADA enzyme activity had regular immune systems .- The serendipitous discovery of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency in two individuals with cellular immune deficiency in 1972 by Dr. Eloise Giblett and colleagues ushered in a new era in the investigation of the molecular mechanisms underlying major immunodeficiency problems.
- In addition, this discovering led to the eventual development of novel therapies not only for ADA deficiency, but also for other immunodeficiency problems and specific leukemias.
- In these days, the only “cure” for severe immunodeficiency diseases was a bone marrow transplant (BMT) from a histocompatible donor.
- However, the gene defects accountable for these devastating problems had been unknown.
- Thus, the patient’s physicians sent blood samples to Dr. Giblett at the King Country Central Blood Bank.
- In the early 1970’s, many major immune deficiency diseases, which includes SCID, X-linked a gamma globulinemia, and Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome, had been well recognized to pediatric immunologists and presumed to be triggered by single gene defects primarily based on patterns of inheritance.
What is the function of adenosine deaminase?
Typically in humans, deamination occurs when an excess in protein is consumed, resulting in the removal of an amine group, which is then converted into ammonia and expelled via urination. This deamination process allows the body to convert excess amino acids into usable by-products.
Why does Deamination occur?
Definition of deaminase. : an enzyme that hydrolyzes amino compounds (such as amino acids) with removal of the amino group.

Comments
Post a Comment